Likewise phenyl cations are unstable thus making s n 1 reactions impossible.
Vinyl halides sn1.
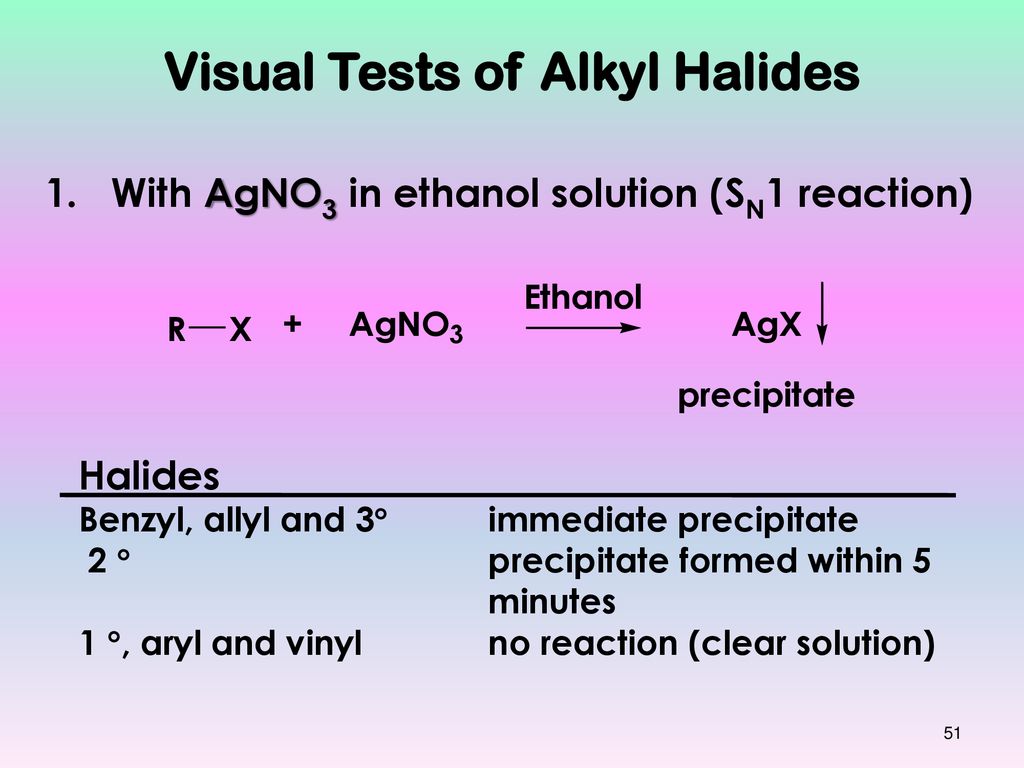
Alkyl halide carbon chain analysis for sn1 sn2 e1 e2 reactions by leah4sci duration.
The substituents around a double bond are within the same plane therefore an s math n math 2 would give steric hindrance.
A sn1 sn2 mechanism on vinyl halide would look like this.
Determine whether each substitution reaction shown below is likely to proceed by an s n 1 or s n 2 mechanism and explain your reasoning.
Nucleophilic substitution via the sn1 or sn2 mechanism does not occur with vinyl chloride or other vinyl halides or aryl halides as it has an unsaturated carbon centre.
In addition the carbon halogen bond is shorter and therefore stronger in aryl halides than in alkyl halides.
Steric hindrance caused by the benzene ring of the aryl halide prevents s n 2 reactions.
A s n 2 b c primary alkyl halide with a strong nucleophile in a polar aprotic solvent.
Sn1 versus sn2 reactions.
Firstly if the nuclophile comes in on the s n 2 path it will bump into a hydrogen or other group which is trans to the leaving group.
My answer was that two reasons exist for why the vinyl halide will not react with a nucleophile.
A s math n math 2 mechanism is not favoured for 3 reasons.
Whether an alkyl halide will undergo an s n 1 or an s n 2 reaction depends upon a number of factors.
So the bond between the chlorine and the carbon in the double bond is much too strong stronger than that of an alkyl chloride to be broken by a nucleophile sn2.
The carbon halogen bond is shortened in aryl halides for two.
Alkyl halides again sn1.
C s n 2 b c secondary alkyl halides favor this.
Use of allyl vinyl acryl aryl iupac jee neet cbse iitian faculty.
3 halides 2 halides and 1 halides 10 15 e2 elimination of vinyl halides converting alkenes to alkynes 10 16 sn1 and e1 reactions unimolecular reactions first order ionization of the alkyl halide r x the rate determining step rate limiting step solvolysis ionization step in detail.
B s n 1 b c tertiary alkyl halide with a weak nucleophile that is also the solvent solvolysis.