The terms geminal and vicinal coupling come under nmr nuclear magnetic resonance and they describe the differences in the nmr peaks when hydrogen atoms undergo coupling differently.
Vinyl hydrogen nmr.
The nmr spectra of vinyl chloride the three dichloroethylenes and trichloroethylene have been obtained and analyzed.
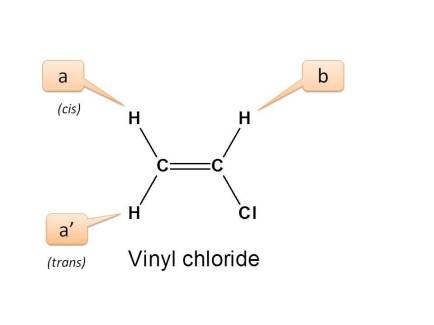
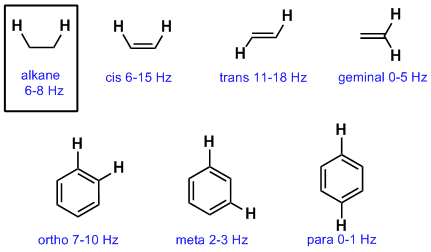
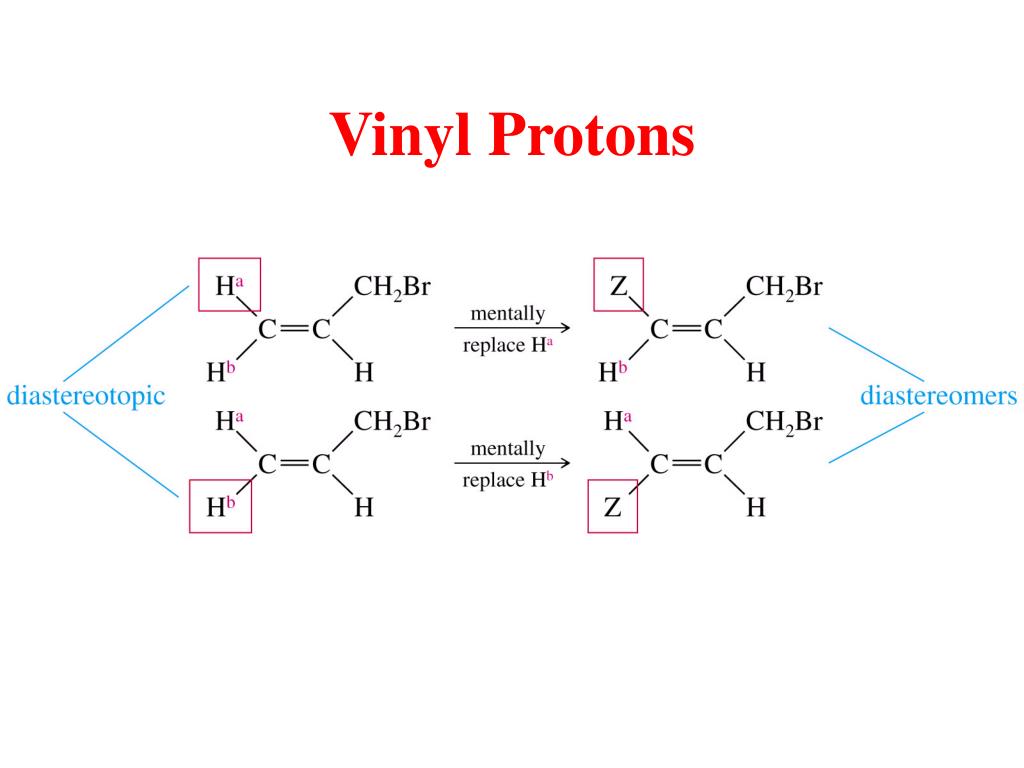
Although there are two protons on one vinyl carbon each h is different because of cis trans relationships.
Typical h nmr shift ranges.
In samples where natural hydrogen h is used practically all the hydrogen consists of the isotope 1 h hydrogen 1.
The c13 h couplings were also obtained for the other chloroethylenes.
Hydrogen atom coupling may occur between two hydrogen atoms that are bound to the same carbon atom or two hydrogen atoms bound to two adjacent carbon atoms.
It describes nuclear magnetic resonance nmr in details relevant to organic chemistry.
None of the other hydrogens are vinylic.
Rather they are each a doublet of doublets which is a direct result of the j values of each proton.
The vinylic hydrogens are shown in red.
A hydrogen atom bonded to an sp 2 carbon of an alkene.
Three deuterated species of vinyl chloride were used to facilitate the analysis and to obtain all the c13 h couplings in this molecule.
0 8 1 5 ppm alkane c h.
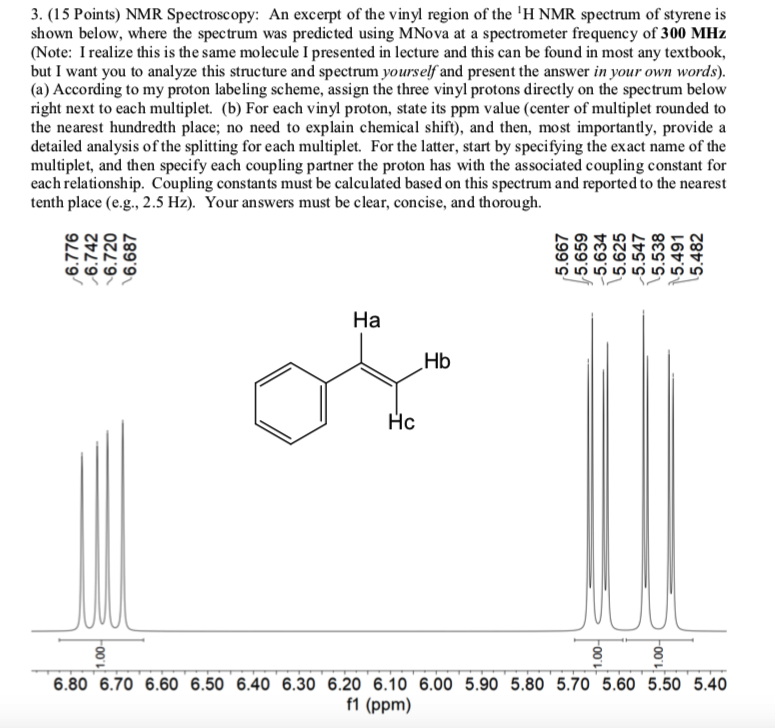
The three inequivalent protons of the vinyl group labeled ha hb and hc do not appear as the type of multiplets we saw above.
This is a general trend add approximately 0 2 0 4 ppm for each additional alkyl group.
Secondary hydrogen tertiary hydrogen vinyl group vinyl.
This set of pages originates from professor hans reich uw madison structure determination using spectroscopic methods course chem 605.
The removed hydrogen atom can be replaced by any group of molecules and it is denoted as r.
The structure of a vinyl group is equivalent to the molecular group when one hydrogen atom is removed from an ethene molecule.
Spectra pdf form of more than 600 compounds are also.
Vinyl aromatics nitriles rocr 3 arcr 2 h alkyne r 3coh o 1h 2nmr shift ranges δ ppm vinyl r 3c f r 3c clrc i r 3c br rccr 3 o δ ppm 13c nmr shift ranges r 2nh r 2ncr h approximate nmr shift ranges note.
Proton nuclear magnetic resonance proton nmr hydrogen 1 nmr or 1 h nmr is the application of nuclear magnetic resonance in nmr spectroscopy with respect to hydrogen 1 nuclei within the molecules of a substance in order to determine the structure of its molecules.
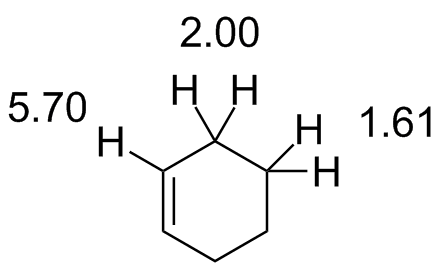
These are typical chemical shifts.
It also includes nmr summary data on coupling constants and chemical shift of 1h 13c 19f 31p 77se 11b.
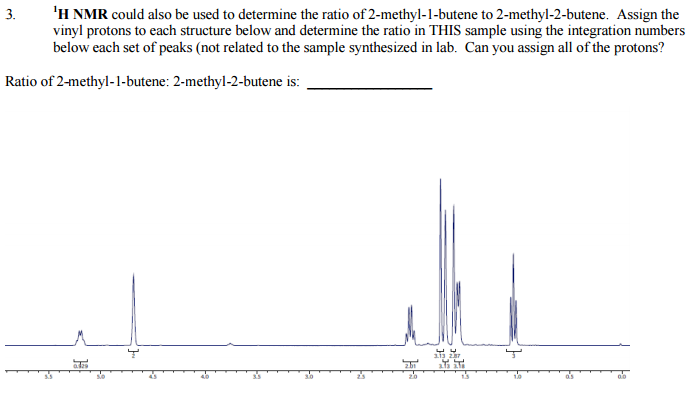
For example consider the regions of the 1h nmr spectrum of vinyl acetate shown below.
Chemical shift d type of proton examples chemical shift in ppm comments.
It contains two sp 2 hybridized carbon atoms and three hydrogen atoms.
The greater the substitution on the carbon bearing the hydrogen the further downfield higher frequency the resonance occurs.
But vicinal coupling refers to the coupling of two hydrogen atoms that are bound to two adjacent carbon atoms.
One h is cis to the carbonyl and the other is.
The vinyl portion of the spectrum hydrogens adjacent to the c c double bond shows three peaks not just two.
























.pdf+-+SumatraPDF_2012-12-21_20-55-11.png)